Jacky
教土豆学计算机
Simple Paxos
Choosing a Value
安全 Safety
-
only a single value may be chosen
-
A server never learn a value has been chosen unless it really has been
活性 Liveness
-
Some proposed value is eventually chosen
-
If a value is chosen, servers eventually learn about it
Among three roles, Acceptor is most important, they decide how to choose a single value.
Problem A: Single Acceptor
The easiest way to choose a value is to have a single acceptor agent. A proposer sends a proposal to the acceptor, who chooses the first proposed value that it receives.
最简单的实现就是只有一个 acceptor. proposer 发送提案给 acceptor, acceptor 选择它接收到的第一个提案 value
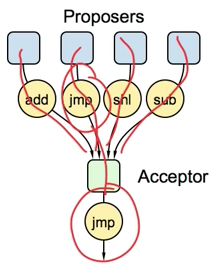 来源: Paxos Lecture
来源: Paxos Lecture
What if acceptor crashes after choosing? 问题是如果 acceptor 在选择一个 value 后崩溃了, 该怎么办?
Solution
So, instead of a single acceptor, we use multiple Acceptors - If one acceptor crashes, chosen value still available.
所以, 为了避免单点故障, 我们使用多个 Acceptors; 如果一个 acceptor 故障, 依然可以继续选择 value.
Problem B: Split Votes
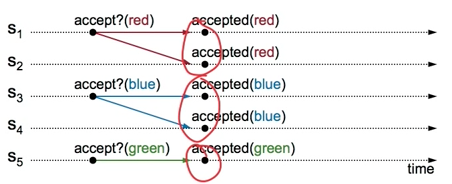 来源: Paxos Lecture
来源: Paxos Lecture
-
Acceptors accepts only first value if receives?
-
If simultaneous proposals, no value might be chosen
有了多个 acceptors 之后, 出现的几个问题是
-
每个 acceptor 都只接受它收到的第一个 value 吗?
-
如果出现多个 proposal, 可能出现 split vote (split brain?)
Solution
-
Acceptors must sometimes accept multiple (different) values
Acceptor 有时必须要接受多个(可能不同) value
-
Value is chosen if accepted by majority of acceptors
value
v被选择仅当它被过半数的 acceptor 所接受
Problem C: Conflicting Choices
-
Acceptor accepts every value it receives?
Accept 应该接受每个它收到的 value 吗?
-
Could choose multiple values
这样会导致有多个不同 value 被选中
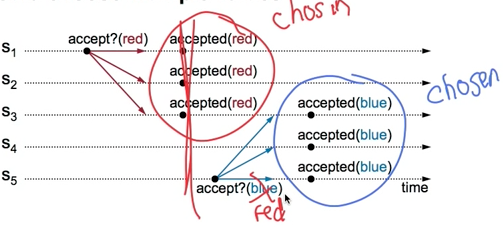 来源: Paxos Lecture
来源: Paxos Lecture
Solution
Once a value has been chosen, future proposals must propose/choose the same value (2-phase protocol)
Conflicting Choice Cont’d
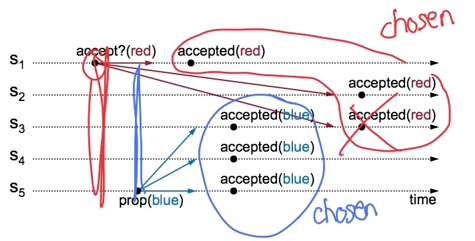 来源: Paxos Lecture
来源: Paxos Lecture
Once we choose one value, any competing proposals have to somehow be aborted that is in this case we somehow need for server 3 to actually reject that red acceptance request after it has already accepted blue and the way we will do this is that we are going to place an order on the proposals where newer proposals take precedence over older proposals.
Solution
- Must order proposals, reject old ones
Proposal Numbers - A way to order proposals
-
Each proposal has a unique number
-
Higher number take priority over lower numbers
-
It must be possible for a proposer to choose a new proposal number higher than anything it has seen/used before
-
-
One simple approach
-
Each server stores
maxRound: the largest Round Number it has seen so far -
To generate a new proposal number: increment
maxRound, concatenate with server id -
Proposers must persistent
maxRoundon stable storage: must not reuse proposal numbers after crash/restart
-
Two Phase approach 二阶段算法
-
Phase 1: broadcast Prepare RPCs 广播 Prepare RPC
-
Find out about any chosen values 获取任何已被选定的 value
-
Block older proposals that have not yet completed 阻止未完结的旧提议
-
-
Phase 2: broadcast Accept RPCs 广播 Accept RPC
- Ask acceptors to accept a specific value 要求 Acceptor 接收 value
Proof
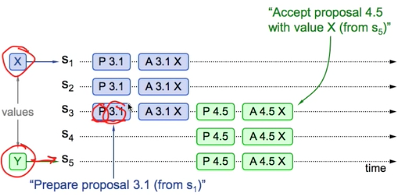
考虑二组 Proposal/Accept, P3.1 A3.1 P4.5 A4.5 交叉的三种可能情形(枚取所有可能的排列)
1 Previous value already chosen
P.3.1 -> A3.1 -> P4.5 -> A4.5
- New Proposer will find it and use it
 来源: Paxos Lecture
来源: Paxos Lecture
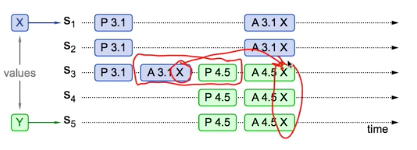
2 Previous value not chosen, but new proposers sees it
P.3.1 -> P4.5 -> A3.1 -> A4.5
-
New proposer will use existing value
-
Both proposers can succeed
 来源: Paxos Lecture
来源: Paxos Lecture
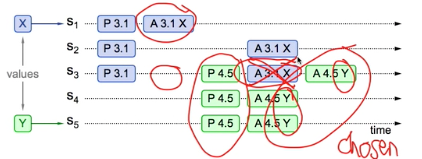
3 Previous value not chosen, and new proposers does not see it
P.3.1 -> P4.5 -> A4.5 -> A3.1
-
New proposer chooses its own value
-
Old proposal blocked (or rejected)
 来源: Paxos Lecture
来源: Paxos Lecture
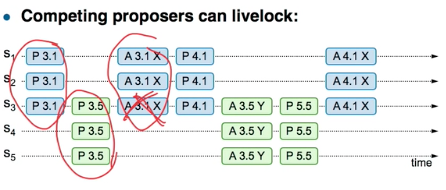
Liveness
 来源: Paxos Lecture
来源: Paxos Lecture
-
One solution: randomized delay before restarting
-
Multi-Paxos will use leader election instead
Configuration Change
Safety requirement
During configuration changes, it must not be possible for different majorities to choose different values for the same log entry.
Leader Election
-
Select one of the servers to act as leader
-
Detect crashes, choose new leader
….
Implementation
 来源: Paxos Lecture
来源: Paxos Lecture
Stable storage, preserved during failures, is used to maintain the information that the acceptor must remember.
Each proposer remember the highest-numbered proposal it has tried to issue, and begins phase 1 with a higher proposal number than it has already used.